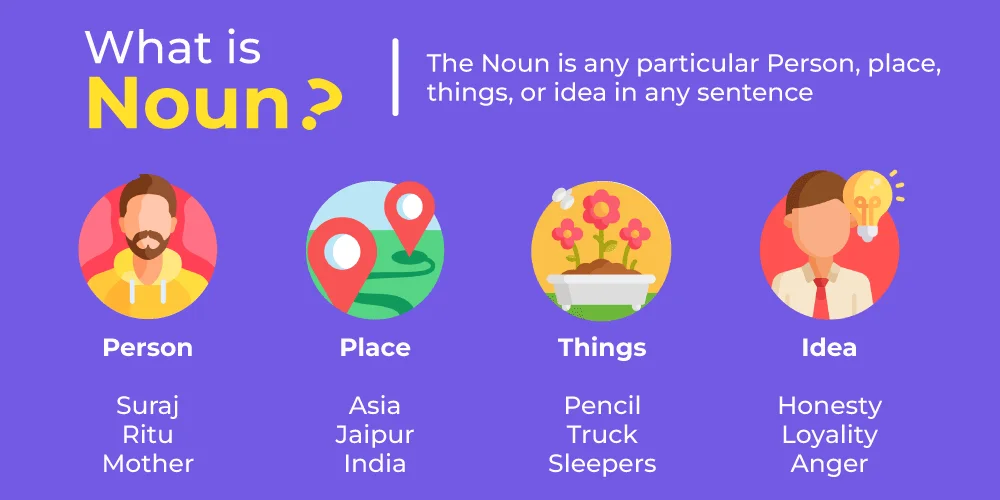
What is a Noun? Types, Definitions and Examples

In simple terms, a noun is a word that names a person, place, thing, or idea. Nouns are one of the basic building blocks of language, and they help us identify and refer to the people, objects, and concepts in our everyday communication. Examples of nouns include “dog” (a thing), “teacher” (a person), “Paris” (a place), and “happiness” (an idea).
A Noun is the name of a Place, Person, or thing. It comes under Parts of Speech, which we have studied in the syllabus of English Grammar.
In this article, We have covered Everything you need to know about Nouns, Their types, Examples and more.
Let’s get a closer look at this.
we can also say Nouns or a word that is the name of something (as a person, animal, place, thing, quality, idea, or action) and that is typically used in a sentence as the subject or object of a verb or as an object of a preposition. Some Examples of Noun include:
Noun Definition
There can be multiple definitions of nouns, we have used the most simple way to define a noun.
Nouns are included in almost every English sentence, and they can be used for a variety of reasons: nouns as subjects, nouns as direct objects, nouns as indirect objects, or nouns as modifiers. There can be multiple more uses of nouns which we will discuss below in the article.
Noun Examples
Here are some examples of nouns:
- Place– Goa, Taj Mahal, Sea, River, Planet, Farmhouse, Tourist place, etc.
- Person– John, Biographer, Cardiologist, Cameramen, Actress, Politicians, etc.
- Things– Grains, Rocks, Trees, Forest, Paper, Glass, Metals, Plastic, etc.
- Ideas– Revolution, Resolution, Invention, Conclusion, Argument, etc.
How are Nouns Used in Sentences?
Nouns can be used as a subject and a verb. The subject in a sentence refers to the person, place, or thing, while the verb describes an action that is being performed by the subject.
Nouns can be used in different components of sentences. We have discussed some uses of nouns as subject, object, and Subject and Object Complements.
1. Nouns as Subjects
The subject of a sentence is the noun or pronoun that acts as an action of the verb.
For Example, in this sentence “The lion chased the goat,”
2. Nouns as Objects
Nouns and pronouns act as a role of objects in a sentence, and both can also be direct and indirect objects in a sentence.
For Example, in this sentence “Raghav is a brilliant student”
3. Nouns as a Direct Object
Noun or Pronoun as a direct object receives the action of the verb.
For Example, in this sentence
4. Nouns as an Indirect Object
Noun or Pronoun as an indirect object is indirectly affected by the action of the verb, usually placed before the direct object.
For Example, in this sentence
5. Nouns as Subject and Object Complements
An object complement is a word or phrase that follows a direct object or renames it. Names, Professions, and Positions act as a role of an object complement.
For Example,
In this sentence, “Green” is the object complement because it follows the direct object “the room” and describes it.
When a noun is used to describe another type of noun. A subject complement can be a noun or noun phrase.
For Example,
In this sentence, “delicious” is used as a subject complement because it follows the linking verb “taste” and describes the subject “
Classification of Noun
The following are the classification of Noun on different basis:
| Noun on different Basis | Types of Nouns | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Type of Noun | Proper Noun, Common Noun, Collective Noun, Material Noun, Abstract Noun | Paris, city, team, water, love |
| Number | Singular Noun, Plural Noun | cat, cats, book, books |
| Function | Subject Noun, Object Noun, Possessive Noun | The dog barks (subject), She loves music (object), John’s car (possessive) |
| Countability | Countable Noun, Uncountable Noun | book, water, ideas |
| Concreteness | Concrete Noun, Abstract Noun | tree, happiness, love |
| Specificity | Proper Noun, Common Noun | Paris, city, person |
| Composition | Compound Noun | toothpaste, bedroom |
Types of Nouns
The following are the different types of noun:
- Proper Noun
- Common Noun
- Collective Noun
- Material Noun
- Abstract Noun
- Singular Noun
- Plural Noun
- Compound Noun
- Countable Noun
- Uncountable Noun
- Concrete Noun
Let us discuss each of the types of Nouns in detail with examples:
1. Proper Noun
A Proper noun is a noun that indicates a specific person or thing that does not require a limiting modifier and is frequently capitalized. It denotes the name of a person, place, or thing.
Examples:
- “John” is a proper noun as it is the name of a specific person
- “Sydney” is a proper noun as it is the name of a specific place
- “Samsung” is a proper noun as it is the name of a specific brand
- “Lassie” is a proper noun as it is the name of a specific pet-animal
- “The Eiffel Tower” is a proper noun as it is the name of a specific landmark
- “The New York Times” is a proper noun as it is the name of a specific newspaper
Facts:
- It’s always written in uppercase
- We never use a/an before it
- It has genders: Masculine, Feminine, Neuter
2. Common Noun
The common noun can be used with a limiting modifier to name a group of people or things or any individual within that group. It denotes the quality possessed by all.
Examples:
- “Tree” – The tree in the front yard is over 100 years old.
- “Book” – I am reading a book about the history of India.
- “Dog” – My dog likes to chase after tennis balls.
- “City” – The city is planning to build a new park.
- “Lake” – We went swimming in the lake last weekend.
- “Person” – That person over there is my friend from college.
- “Car” – The car’s engine makes a strange noise when it starts up.
Facts:
- Common nouns are divided into countable and uncountable
- We always use a/ an before singular countable noun
3. Collective Noun
Collective Noun denotes the collection of people, things, or animals.
Examples:
1. Collective nouns for groups of animals:
- A herd of cattle
- A flock of birds
- A pack of wolves
- A school of fish
2. Collective nouns for groups of people:
- A crowd of people
- A group of friends
- A team of athletes
- A gang of thieves
3. Collective nouns for things/objects:
- A pile of rocks
- A stack of books
- A bundle of sticks
- A cluster of grapes
4. Material Noun
A material noun refers to a material or substance that is used to make things. It denotes the base features of the materials.
Examples:
- “The desk was made of solid oak.” (oak is a material noun)
- “She wore a gold necklace to the party.” (gold is a material noun)
- “The bridge was constructed with steel girders.” (steel is a material noun)
- “He built a fire using dry branches and twigs.” (branches and twigs are material nouns)
Facts:
- We never use a/an before it because it is uncountable
- We never make the plural of it by adding s/es
5. Abstract Noun
A noun expressing anything immaterial and abstract defines an abstract noun. Another prevalent interpretation of abstract nouns is that they refer to entities that are not visible to the naked eye. It denotes mental state, feelings, and emotions.
Abstract nouns cannot be seen, smelled, heard, tasted, or touched. Intangible entities that do not exist as physical objects are referred to as abstract nouns.
Examples:
- Love: She felt a deep love for her family.
- Courage: His courage in the face of adversity was admirable.
- Intelligence: She has a high level of intelligence.
- Success: His success in business was due to his hard work.
Facts:
- We never use a/an before it because it is uncountable
- We never make the plural of it by adding s/es
- Abstract nouns can be made from the conversion of verbs and adjectives
6. Singular Noun
Singular Nouns are those Nouns that denote a single or one person, one place, or one thing. Let us understand it with some examples.
Examples:
- “The cat slept on the windowsill.” (Singular noun “cat” refers to one animal)
- “She read a novel before bed.” (Singular noun “novel” refers to one book)
- “He took a single cookie from the jar.” (Singular noun “cookie” refers to one baked good)
- “The apple was red and shiny.” (Singular noun “apple” refers to one piece of fruit)
- “The car needs an oil change.” (Singular noun “car” refers to one vehicle)
Facts:
- We use a/an before the Singular Noun.
- We can make the plural of it by adding s/es
So, Singular Noun is all about the quantity of Place, Person, or Thing, which counts will always be one. In other words, we can say that Singular Nouns mean only one Person, Place, or Thing.
7. Plural Noun
A Plural noun is a noun that indicates multiple People, Places, Animals, or Things. They can be easily made Plural by adding easily s, es or making changes in the spelling of a Singular Noun.
Examples:
- “The dogs barked loudly.” (dogs is a plural noun)
- “She bought a dozen eggs.” (eggs is a plural noun)
- “The children played in the park.” (children is a plural noun)
- “We saw several deer in the woods.” (deer is a plural noun)
Facts:
- It’s always written in uppercase
- We never use a/an before it
- It has genders: Masculine, Feminine, Neuter
8. Compound Noun
A compound noun is simply made up of two or more word that comes together to form a noun i.e. Policeman, Greenhouse, Bluebird, Smartphone.
Examples:
- “Bookshelf” (Book + Shelf) – The bookshelf was filled with old books.
- “Raincoat” (Rain + Coat) – I am going to wear my raincoat because it’s going to rain.
- “Haircut” (Hair + Cut) – He got a new haircut.
- “Bedroom” (Bed + Room) – I am going to sleep in my bedroom tonight.
Facts:
- It is not necessary that both words are Nouns.
- It is formed with the help of more than one part of speech.
9. Countable Noun
Countable Nouns are those nouns that can be easily counted. These nouns can be singular or plural.
Examples:
- “I have two cats.” (cats – countable noun)
- “She bought a loaf of bread.” (loaf – countable noun)
- “He owns several cars.” (cars – countable noun)
- “We need to buy some eggs.” (eggs – countable noun)
- “The class has only five students.” (students – countable noun)
Facts:
- We can use words like some, any, a few, many, and a number of, with countable Nouns.
- It can be singular and plural too.
- It can be preceded by the indefinite article a or an.
- It can also be preceded by a number.
10. Uncountable Noun
Uncountable Nouns are those Nouns that can’t be counted. These nouns are always in singular form but can’t be counted. Nouns like sugar, rice, water, hair, and stars.
Examples:
- “Information” – Can you provide me with more information about the project?
- “Water” – Water is essential for human survival.
- “Furniture” – The furniture in the room needs to be rearranged.
- “Luggage” – I can’t find my luggage at the baggage claim.
11. Possessive Noun
A possessive noun is a noun that shows ownership or possession of something. It is formed by adding an apostrophe + “s” to the noun.
Examples:
- The dog’s bone (shows that the bone belongs to the dog)
- The children’s toy (shows that the toy belongs to the children)
- The company’s profits (shows that the profits belong to the company)
- The teacher’s desk (shows that the desk belongs to the teacher)
Facts:
- Possessive nouns are formed by adding an apostrophe and the letter “s” to the noun, or just an apostrophe if the noun is already plural and ends in “s”.
- Possessive nouns can be singular or plural, and they can indicate possession by one person or thing or by multiple people or things.
- Possessive nouns can be used to indicate a relationship between two nouns, such as “the dog’s ball” (showing that the dog possesses the ball)
- Do not use an apostrophe with possessive pronouns such as “its”, “hers”, “yours”, “theirs”, “ours”, and “mine”.
12. Concrete Noun
A concrete noun is a noun that refers to a physical object that can be perceived through the five senses. These senses are sight, hearing, touch, taste, and smell. Examples: Dog, building, tree, chair, etc.
Examples:
- Possessive nouns are formed by adding an apostrophe and the letter “s” to the noun, or just an apostrophe if the noun is already plural and ends in “s”.
- The dog barked at the mailman. (“dog” – concrete noun)
- The building was made of red bricks. (“building” – concrete noun)
- Roses in the garden are beautiful. (“Roses” – concrete noun)
- The tree was so tall that it touched the sky. (“tree” – concrete noun)
Noun Phrases
A Noun Phrase means a group of words that acts as a Noun. There are 4 types of Noun phrases.
- Determiners: A, my, the, his, her, etc.
- Possessive Determiners: Your, My, His, Her, etc.
- Quantifiers: Some, More, All, Few, etc.
- Numerals: One, Two, Three, Four, etc.
Examples:
- “The red sports car” – The noun phrase is “the red sports car” and it is used as the subject of the sentence “The red sports car is fast.”
- “The little girl with the curly hair” – The noun phrase is “the little girl with the curly hair” and it is used as the subject of the sentence “The little girl with the curly hair is singing a song.”
- “My favorite book” – The noun phrase is “my favorite book” and it is used to indicate possession in the sentence “I am reading my favorite book.”
- “The city of Paris” – The noun phrase is “the city of Paris” and it is used as the subject of the sentence “The city of Paris is known for its art and culture.”
Proper Noun vs. Common Noun
| Proper Noun | Common Noun |
|---|---|
| Proper Nouns include Specific People, Places, or Things. | Common Noun means generic place, person, or things. |
| Proper Nouns are Specific. | Common Nouns are Non-specific. |
| Proper Noun is often capitalized. | Common Nouns are usually not capitalized. |
| For Example- Japan, Salman, Satluj River, Parker Pen, etc. | For Example- River, Grandfather, Tree, Pen, Pencil, etc. |
Multifunctional Nouns
Nouns can also be used in other ways. Some of the most common multifunctionality of nouns can be seen when a noun is used as a verb and a noun is used as an adjective.
1. Noun used as Verbs
Nouns can also be used a verb in sentences, this is also called verbing or denominalization. You can use nouns as verbs with slight changes in spelling.
Examples:
I used the hammer to drive the nail into the wood. (hammer used as a noun)
- The carpenter hammered the nails into the wood. (hammered used as a verb)
I poured a glass of water for my thirsty dog. (water used as a noun)
- The farmer watered the crops to help them grow. (watered used as a verb)
2. Noun used as Adjectives
Nouns can also be used as Adjectives to describe other nouns, this is also called adjectival use or attributive use of nouns.
Examples:
The student eagerly absorbed the information presented in class. (Student used as a noun)
- The student’s enthusiasm for learning was contagious. (Used as Adjective)
The musician performed a mesmerizing melody that filled the room with sound. (Used as a noun)
- The musician’s talent was undeniable. (Used as Adjective)
FAQs on Noun and it’s types
A Noun can be defined as a Place, Person or Thing. For Example: City, Sea, Paper, Wood, Laptop, Plastic, Iron etc. are known as Noun.
There are Ten Types of Nouns, which are:
- Proper Noun – Agra, Abhinav, Aluminium etc.
- Common Noun – Priest, People, Girls, Boys, Metals, Capitals etc.
- Collective Noun – Common People, Analog watch, Gold ring, etc.
- Material Noun – Sugar, Sand, Fertilizers, Honey, Cardboard etc.
- Abstract noun – Love, Hate, Compassion, Forgiveness, etc.
- Singular Noun – Woman, Child, Boy, Girl, Man, Wife, Knife etc.
- Plural Noun – Women, Children, Boys, Men, Wives, Knives etc.
- Compound Noun – Paperweight, Milkman, Tennis court etc.
- Countable Noun – Eyes, Sun, Gifts, Papers, Floors, rods, etc.
- Uncountable Noun – Hairs, Stars, Water, Milk, Feelings like Love, Hate etc.
A Noun can also act as a verb and as an adjective too. For Example: Money is a Noun while Money-minded is an adjective.
Improvement, Quality, Courage, Optimism, etc.
A noun is a word that represents a person, place, thing, or idea, while a pronoun is a word that replaces a noun.
Examples:
- Noun: “The cat” (cat is a noun)
- Pronoun: “it” (it is a pronoun that replace the noun cat)
- Noun: “The boy” (boy is a noun)
- Pronoun: “He” (he is a pronoun that replaces the noun boy)
Countable Nouns can be Singular or Plural while Uncountable Nouns can’t be counted.
Nouns are words that represent people, places, things, or ideas. They can be identified by their role in a sentence, being preceded by articles or determiners, or by having a plural form.
Examples: “dog” in “The dog barked,” “John” and “store” in “John went to the store,” “book” in “She read an interesting book.”
Countable nouns are nouns that can be counted as individual units. They refer to things that can be perceived as separate and distinct entities. Examples of countable noun Includes such as “dogs,” “books,” “cities,” “ideas,” or “teams.” etc
Uncountable nouns are things that cannot be counted individually. They represent substances, concepts, or qualities as a whole. Examples include “water,” “knowledge,” and “happiness.”
A noun clause is a type of dependent clause (a group of words with a subject and a verb) that functions as a noun within a sentence. It can act as the subject, object, or complement of the main clause. Noun clauses often begin with words like “that,” “if,” “whether,” “who,” “whom,” “what,” “how,” and “why.”
Quý anh/chị đang tìm kiếm một doanh nghiệp uy tín cung cấp dịch vụ Công Nghệ Thông Tin như Thiết kế và lập trình website, Digital Marketing, hoặc dịch vụ Bảo trì và chăm sóc hệ thống máy tính, ...? Đừng ngần ngại hãy liên hệ với The ÂN qua số điện thoại (+84).326.418.478 để được tư vấn cụ thể, hoặc liên hệ qua mẫu tin.
Các thông tin nổi bật khác: